As per the IDC‘s prediction, “unstructured data will represent 80% of data worldwide by 2025.”
A majority of the data is unstructured in the 21st century. As your business grows, imagine the exponential growth of unstructured data with no particular schema. With a distributed storage system, you already have choices with block storage or object storage format. But the question is which flexible and affordable data storage format should you rely on going forward?
Think about the massive Petabyte-scale applications. What if you run out of storage capacity? For data archiving, adding a new shelf of commodity drives (disks) in filesystems will only increase the storage costs. Besides, it requires extensive planning as complex hierarchies fail to support storage capacities. Again, maintenance & disk performance concerns add up. This approach is labor-intensive and no doubt, way too expensive.
Luckily, cloud object storage format is one such cost-effective method for scaling your unstructured data. So, what makes this storage so attractive for the cloud users? Let’s check out.
What is Object Storage?
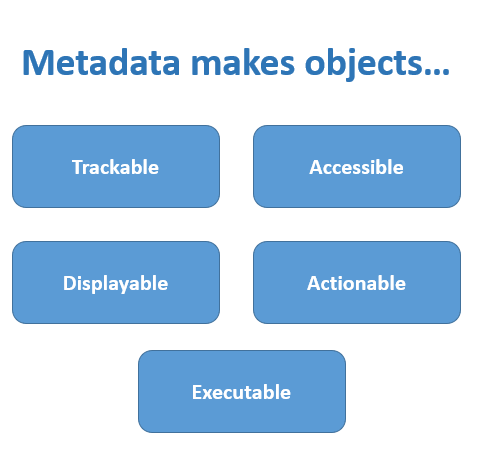
To put it simply, Object storage is a storage architecture that stores files as objects instead of blocks. It is a method of storing unstructured data in a structurally flat file system distributed across locations. In this format, the file space composes metadata tags that support simple APIs to describe, read, delete, and locate the object. As a result, you can directly access the data kept on any device via the API protocol. Such metadata tags include unique identifiers that facilitate better identification and classification of data.
Interestingly, such an approach can scale to petabytes of data by aggregating storage into grid storage structures that undertake load distribution. Another key point is that these meta tags are highly customizable that lets you easily organize, access, retrieve all the data by tracking and indexing files whenever required. Object storage service can be implemented at the device level, system level, and even at the interface level. The data stored as objects ensures data availability, searchability, and enhanced data security as it protects the data against accidental deletion or corruption.
Object Storage – Use Cases
Some of the popular use cases of object-based storage systems are:
- Unstructured data that includes music, videos, images, and multimedia files,
- Pharmaceutical and financial data,
- Backup, database dumps, and log files,
- Archived files, media assets,
- Historical data sets of diverse nature; and,
- Sensor data.
Now that you know what object storage is, let’s delve deeper and understand how it works?
How Object Level Storage Works?
Unlike relational databases with rows & columns, object-based storage architecture stores units of data in a structurally flat data environment. Each object stored includes metadata with description and unique identifiers that stores data linked across geographically dispersed nodes.
This storage system can scale out endlessly by adding nodes. Because this approach lets you configure automatic routing of data to the right storage systems. As a result, you locate objects even if it is not stored in the same physical location. Again, the object storage platform is designed to be “eventually consistent,”. So, any app can find the updated data across the entire Object Store over time.That is to say, finding the latest file without searching through the file systems is just at your fingertips! Another excellent perk of using such storage type is that you can maximize the disk size to scale up data to several hundred petabytes stored in a single namespace. Currently, with added features, object storage solution is the most balanced architecture through which you can achieve storage scalability without compromising on performance.
If you are a storage admin responsible for scaling data to a petabyte range, you are sitting in the hot seat! Because, you need to maximize usable space for data storage. Indeed, you are spoilt for a choice with approaches such as SAN and NAS systems, Scale-out file systems or the public cloud. But, each approach has it’s own set of complexities, performance and data privacy concerns. This is where object storage comes in. So, who are the major providers of cloud object storage? Let’s check out.
Object Storage Options in the Cloud
Amazon S3 –
Amazon’s S3 is one of the best open-source object storage media and a distributed service for on-premise and private cloud deployment that provides 99.999999999% durability. Interestingly, the AWS storage stores data as objects within resources called buckets. Since, each object in S3 is identified by a bucket, a key, and a unique version ID, you can easily organize data on the right storage tier that can be accessed and retrieved anytime from anywhere. Also, you can store data in a native format and manage storage in one place.
Amazon Glacier –
AWS Glacier is a widely supported AWS solution that provides S3’s scalable storage infrastructure in the cloud to scale up much faster. Apart from providing robust and comprehensive security, Amazon glacier can store long-term data allowing you to access archives whenever you need. However, it’s not the best option for frequently accessed data. But the best part of AWS glacier is that this solution satisfies all the compliance standards to meet stringent regulatory requirements.
Azure Storage –
Another popular cloud provider service is Microsoft Azure. Since Azure supports multiple storage account types with unique features, you can easily store data in blob storage with tiered storage. Such storage is ideal to build powerful cloud-native and mobile apps. Azure storage analytics lets you trace, monitor, and diagnose data of storage accounts to perform log analytics for workloads. Also known as blob storage, this storage supports tiers such as:
- hot (frequently accessed data),
- cool (infrequently accessed data); and
- archive (rarely accessed data) access tiers.
Google Cloud Storage –
Another great alternative to store data is Google cloud object storage (GCP) that supports terabyte size of data on individual objects. GCP storage supports four types of storage tiers:
- Standard (frequently used data),
- Nearline (infrequently used data),
- Coldline (rarely used data), and
- Archive (long-term storage data).
Now that you know some of the best cloud services, take a sneak peek at the top benefits of object-based storage.
Key Benefits of Object Storage
Some of the important benefits of the object-based storage architecture are:
Robust Accessibility –
Since object storage supports metadata, you can easily add metatags to track and index files across locations. That’s a huge technical advantage because you get to manage unstructured data without the need of any additional software. So now, with the opportunity of analytics to build, modify, and deploy systems or developing major operating systems, the possibilities are endless!
Infinite Storage –
In the first place, distributed storage systems have an infinitely scalable flat structure with no dependency on hardware or software i.e., not restricted to a single server or NAS. So, you can keep adding nodes to scale up to any number of custom attributes. There are no limits! And the best part is that you can build massive unstructured data stores without any administrative overhead.
Cost-effective Solution –
Unlike other storage options, object-based storage device provides a distributed model across multiple servers. Now the guesswork gets simple! You can lower the equipment and management costs drastically and manage multiple racks of storage within one entity. In addition, you don’t have to compromise on security and data integrity. Furthermore, you pay for what you use which makes it a great choice for public cloud storage. Additionally, if you have private cloud object storage or space, the cost is even lower!
Long-term Data Protection –
With object storage services (Amazon S3, Azure Blob), you can store data in cloud tiers that support encoding & replication. This ensures long-term and cost-effective data protection.
Faster Data Retrieval –
Data retrieval is faster with unrestricted metadata and ID numbers. This makes the life of storage administrators much easier because they can search files through metadata much faster.
Note: Object storage system surely has its distinct advantages. But, it’s not suitable for traditional databases as writing objects is a slower process. Moreover, you cannot modify object-based modular units as it is designed to write files to object storage only once.
Which Object Storage Open Source Platform Should you Choose?
As a matter of fact, you have plenty of choices for open-source platforms that implement cloud object storage software in the data center. But, before you invest in a third-party platform, you must conduct an extensive research. A quick look at these questions is worth any administrator’s consideration:
- Do the features & benefits of the object-based storage systems fit your organizational needs?
- Should you deploy hardware, or software-based object storage, or a combination of both?
- Which type of data encryption protection can enhance security for the cloud and on-premise?
- Which is the best cost-effective storage for static retrieval of unstructured data?
The answers to these questions can make a difference big time! That’s because every object storage type is different based on its complex setup procedures. But to achieve efficient backup & recovery without losing data to recovery timeframe, you need to sit back and relax! Because Zmanda is here to solve businesses’ common storage pain points.
Zmanda Helps You Make a Better Choice
To do it right, Zmanda delves deeper into object-based storage architecture. By integrating data protection solutions Zmanda can simplify your data backup and management while reducing storage costs drastically.
- Through robust native integrations with Amazon’s Simple Storage Service (S3) and S3 compatible service providers, PostgresSQL backup and storage, OpenStack Swift, Azure object storage, google cloud object storage, Zmanda’s support for object storage software provides infinite capacity for scale-out infrastructure and easy management for any workloads. So now, you can store your data across a host of storage mediums – either on cloud or long-term tape media, on-prem NAS/SAN environments, disks, or local storage.
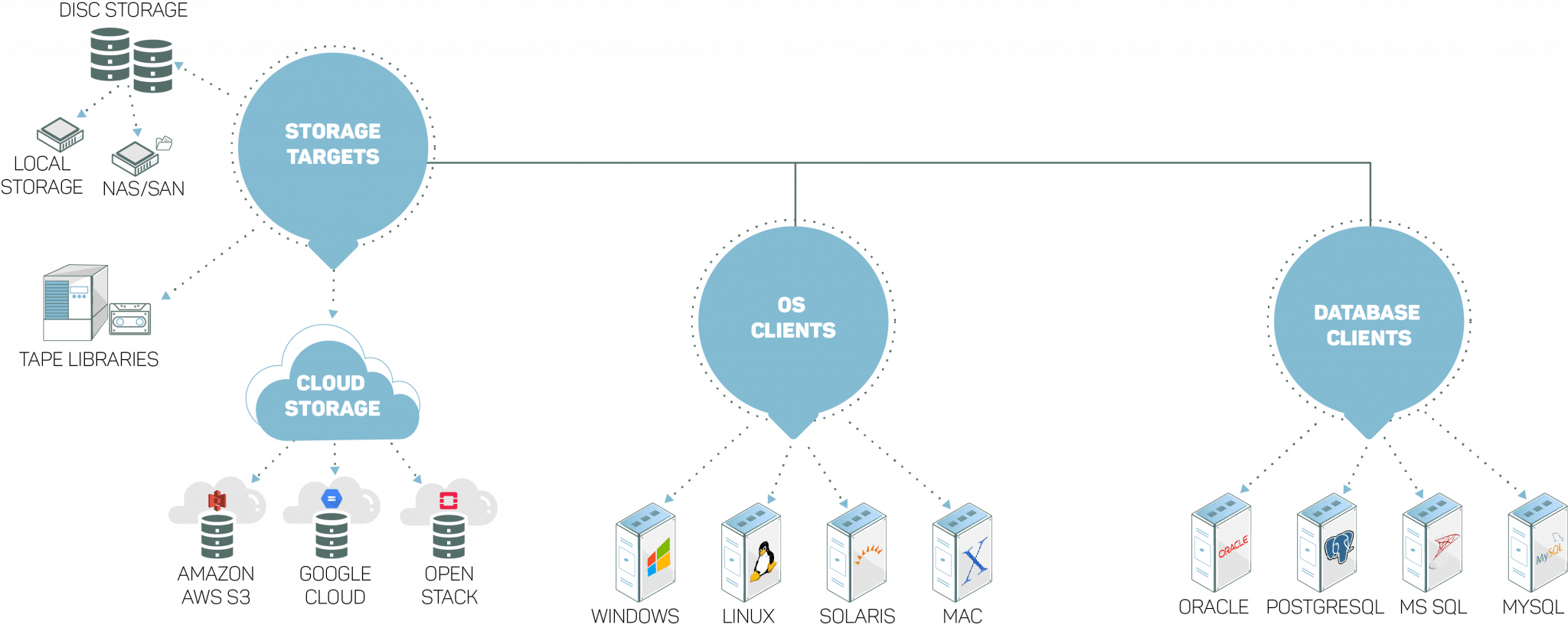
- Built on proven layered security architecture, Zmanda offers the most cost-effective solution that maximizes backup performance without breaking the bank.
- As an open-source and enterprise backup software, you have enough opportunities to leverage integrated cyber protection to backup, archive, and retrieve petabyte-scale data at any time, anywhere.
Planning for your enterprise terabytes to exabytes? Get in touch with us to know how we get the best possible mileage for all your enterprise storage needs.


